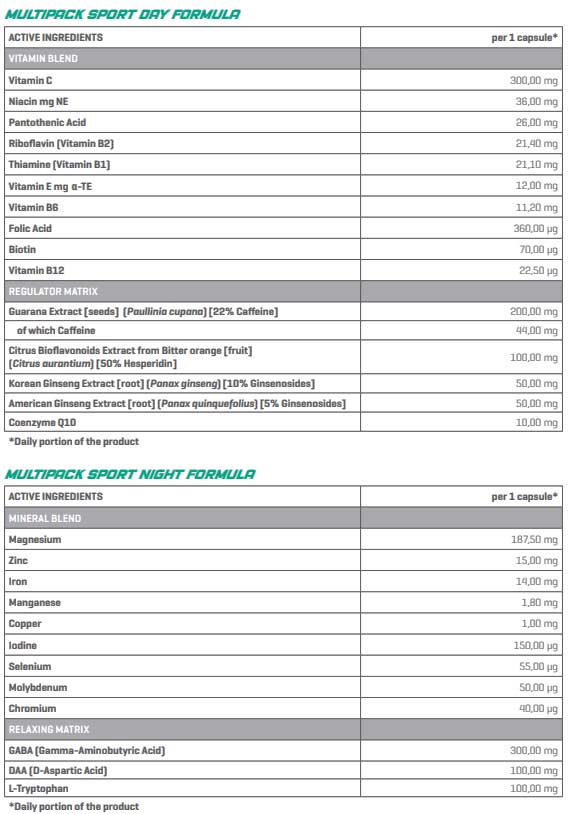
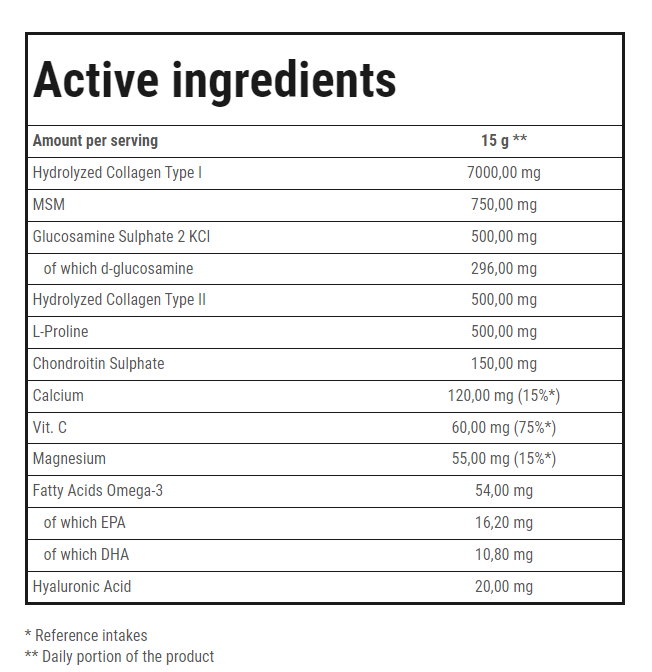
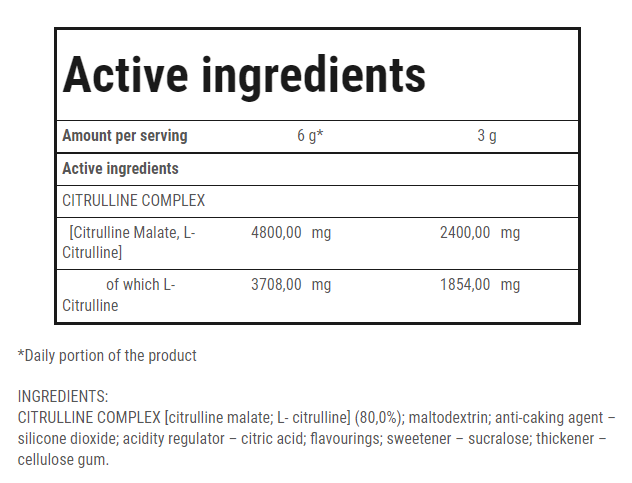
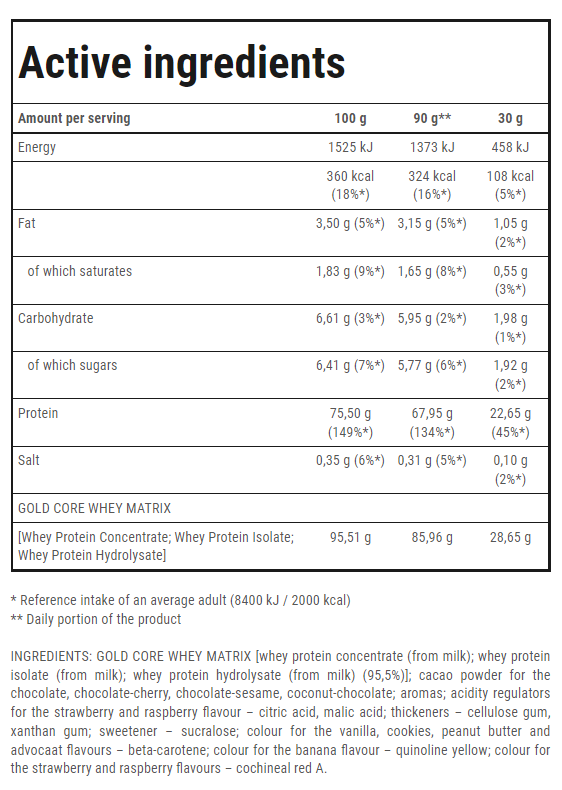
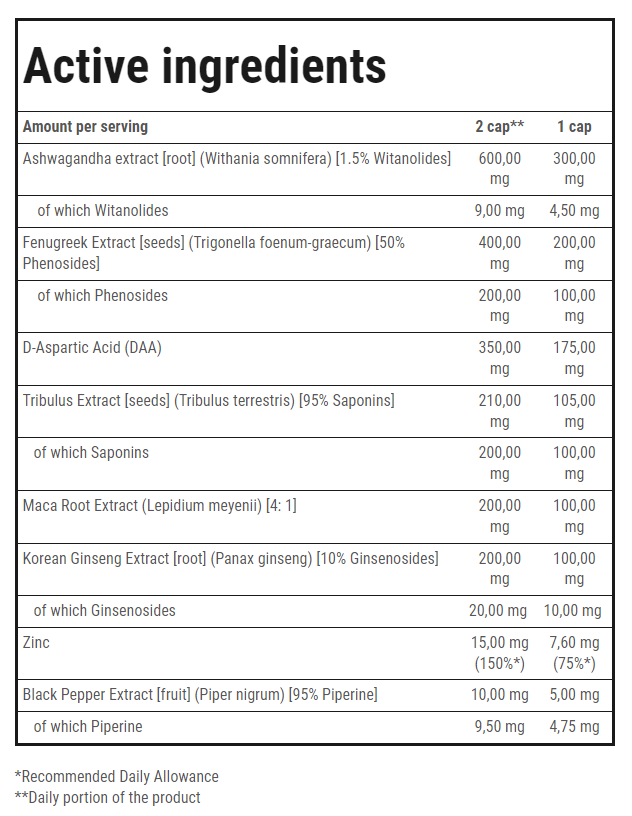
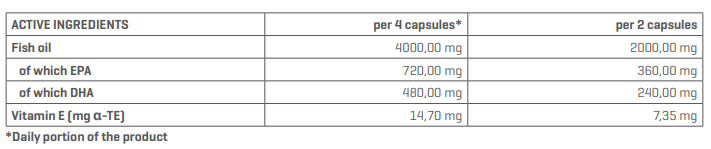
WHEY PROTEIN – EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW

WHEY PROTEIN – WHERE IT COMES FROM AND HOW IT IS OBTAINED
Whey protein is one of the protein fractions found in milk. Milk itself does not belong to high protein products (about 2% of protein), but the value of whey proteins it contains is very high. The milk protein group consists of casein and whey proteins. Whey proteins make up about 12- 15% of the total milk protein group. During the production of various milk products, the casein clot first precipitates. A casein protein strain is concentrated in this isolated solid part of the milk. The remaining liquid part is whey itself. It extracts whey proteins, which constitute only about 1% of its composition.
Highly concentrated whey protein products are obtained from whey, using membrane technologies. Their production is safe for whey proteins, that are very sensitive to damaging factors. This is particularly true of high temperature, which can lead to an irreversible change in their structure (denaturation). Then, the protein is unfortunately not assimilable. And, as it turns out, whey protein concentrates are not only high quality proteins, but also carriers of many health-promoting substances.
WHY WHEY PROTEIN HAS SPECIAL NUTRITIONAL VALUES
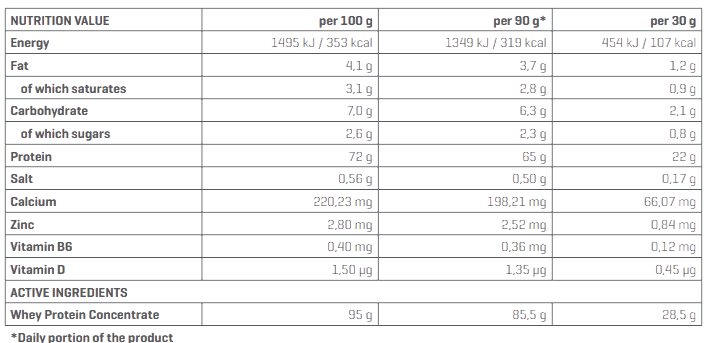
Important: Whey protein is a wholesome protein, showing maximum assimilability. Its additional advantage is the high content of BCAA and glutamine amino acids. Whey protein satisfies the appetite and provides glycomacropeptide, regulating the digestive system.
It is a wholesome protein. This means that it contains all 8 exogenous amino acids (i.e. those that the body is unable to produce on its own) in the right proportions. Thanks to this protein is fully absorbed by the human organism. Whey protein belongs to proteins that do not cause digestive problems. It owes it to the unique amino acid composition and almost zero amount of lactose, which is removed during the production of protein nutrients.
The advantage of whey proteins is the high content of branched chain amino acids (BCAA) and glutamine, which are essential amino acids associated with effort.
Due to elimination of high temperature from the production of high-protein nutrients, they are the carrier of valuable health-promoting substances in which milk is abundant. These will include peptides that prevent the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II- a part of the RAA system (renin- angiotensin- aldosterone). These substances are related to the body’s water management and pressure regulation. The cascade of changes in this system causes vasoconstriction, and in excess it can stimulate the development of hypertension.
Whey proteins will also carry glycomacropeptide. This compound is responsible, among others, for improving the composition of the intestinal microflora and the emission of tissue hormones in the digestive system, which reduce the feeling of hunger.